- Recommended name
- Portimine A
- Synonyms
- Portimine, Portimine-A
- Recommended acronym
- Port-A
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
- Name
- Vulcanodinium rugosum
- Note
- Portimine A production was initially reported in V. rugosum strains from New Zealand and France but later all strains were shown to produce portimine A, irrespective of their origin or pinnatoxin profile. Selwood, A.I., Wilkins, A.L., Munday, R., Shi, F., Rhodes, L.L., Holland, P.T., 2013. Portimine: a bioactive metabolite from the benthic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum. Tetrahedron Lett. 54(35), 4705-4707. Geiger, M., Desanglois, G., Hogeveen, K., Fessard, V., Leprêtre, T., Mondeguer, F., Guitton, Y., Hervé, F., Séchet, V., Grovel, O., Pouchus, Y.F., Hess, P., 2013. Cytotoxicity, fractionation and dereplication of extracts of the dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum, a producer of Pinnatoxin G. Mar. Drugs 11(9), 3350-3371.
Vector Species
- Name
- Mytilus galloprovincialis
- Note
- Hort, V., Bastardo-Fernandez, I., Nicolas, M., 2023. Exploration of Vulcanodinium rugosum Toxins and their Metabolism Products in Mussels from the Ingril Lagoon Hotspot in France. Mar. Drugs 21(8), 20. Hort, V., Bourcier, S., 2024. Discovery of a series of portimine-A fatty acid esters in mussels. Harmful Algae 134, 102621.
References
- Selwood et al., 2013
- Selwood, A.I., Wilkins, A.L., Munday, R., Shi, F., Rhodes, L.L., Holland, P.T., 2013. Portimine: a bioactive metabolite from the benthic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum. Tetrahedron Lett. 54(35), 4705-4707.
- Hort et al., 2023
- Hort, V., Bastardo-Fernandez, I., Nicolas, M., 2023. Exploration of Vulcanodinium rugosum Toxins and their Metabolism Products in Mussels from the Ingril Lagoon Hotspot in France. Mar. Drugs 21(8), 20.
- Hort et al., 2024
- Hort, V., Bourcier, S., 2024. Discovery of a series of portimine-A fatty acid esters in mussels. Harmful Algae 134, 102621.
- Geiger et al., 2013
- Geiger, M., Desanglois, G., Hogeveen, K., Fessard, V., Leprêtre, T., Mondeguer, F., Guitton, Y., Hervé, F., Séchet, V., Grovel, O., Pouchus, Y.F., Hess, P., 2013. Cytotoxicity, fractionation and dereplication of extracts of the dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum, a producer of Pinnatoxin G. Mar. Drugs 11(9), 3350-3371.
- Structure
-
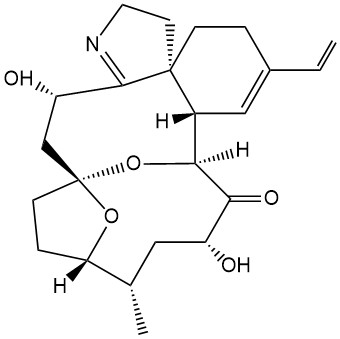
- Formula
- C23H31NO5
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 401.22022
- Molfile
- see chemfiles
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- C=CC1=C[C@@]([C@]2([H])O3)([H])[C@]4(CCN=C4[C@@H](O)C[C@@]3(CC5)O[C@]5([H])[C@@H](C)C[C@@H](O)C2=O)CC1
- Alternative SMILES
- n/a
- InChi key
- JYQBXOZZPLFICX-DSUQWPNCSA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C23H31NO5/c1-3-14-4-6-22-8-9-24-21(22)17(26)12-23-7-5-18(28-23)13(2)10-16(25)19(27)20(29-23)15(22)11-14/h3,11,13,15-18,20,25-26H,1,4-10,12H2,2H3/t13-,15+,16+,17-,18-,20-,22+,23-/m0/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- Unknown
- Chem files
- chemfiles/Port-A.cdxml chemfiles/Port-A.mol
References
- Selwood et al., 2013
- Selwood, A.I., Wilkins, A.L., Munday, R., Shi, F., Rhodes, L.L., Holland, P.T., 2013. Portimine: a bioactive metabolite from the benthic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum. Tetrahedron Lett. 54(35), 4705-4707.
- Tang et al., 2023
- Tang, J., Li, W., Chiu, T.Y., Martínez-Peña, F., Luo, Z., Chong, C.T., Wei, Q., Gazaniga, N., West, T.J., See, Y.Y., Lairson, L.L., Parker, C.G., Baran, P.S., 2023. Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity. Nature 622(7983), 507-513.
- Certified
- False
- Certified links
-
-
n/a
- Non certified reference material
- True
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
- Regulatory status
- False
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- n/a
- Organ system toxicity
- Dermatotoxicity
- Risk assessment
- Unknown
- Molecular targets known
- True
- Molecular targets
- Inflammation (NLRP1)
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- Unknown
- TEF available
- False
- Notes
- Portimine A was initially described by Selwood et al., 2013, who also showed that it is not very toxic to mice via intraperitoneal injection but highly cytotoxic. A parallel publication (Geiger et al., 2013) also confirmed its highly cytotoxic character and found it isobaric with three other natural products (nakijiquinone A, stachybotrin A and N-carboxy-methyl-smenospongine). Its structure was later confirmed through chemical synthesis by Tang et al., 2023, who also proposed its use as anticancer drug due to the apoptotic character in several cell lines. The inflammatory character was demonstrated by Gorse et al., 2025, explaining the skin damage observed in bathing people in Cuba in 2015 (Moreira-Gonzalez et al., 2021) and in artisanal drift-net fishermen in Senegal in 2020 and 2021. Until 2025, all strains of Vulcanodinium rugosum have been shown to produce portimine A, irrespective of their profile of pinnatoxins (or the absence of pinnatoxins).
References
- Selwood et al., 2013
- Selwood, A.I., Wilkins, A.L., Munday, R., Shi, F., Rhodes, L.L., Holland, P.T., 2013. Portimine: a bioactive metabolite from the benthic dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum. Tetrahedron Lett. 54(35), 4705-4707.
- Geiger et al., 2013
- Geiger, M., Desanglois, G., Hogeveen, K., Fessard, V., Leprêtre, T., Mondeguer, F., Guitton, Y., Hervé, F., Séchet, V., Grovel, O., Pouchus, Y.F., Hess, P., 2013. Cytotoxicity, fractionation and dereplication of extracts of the dinoflagellate Vulcanodinium rugosum, a producer of Pinnatoxin G. Mar. Drugs 11(9), 3350-3371.
- Moreira-Gonzales et al, 2021
- Moreira-Gonzalez, A.R., Comas-Gonzalez, A., Valle-Pombrol, A., Seisdedo-Losa, M., Hernandez-Leyva, O., Fernandes, L.F., Chomerat, N., Bilien, G., Herve, F., Rovillon, G.A., Hess, P., Alonso-Hernandez, C.M., Mafra, L.L., 2021. Summer bloom of Vulcanodinium rugosum in Cienfuegos Bay (Cuba) associated to dermatitis in swimmers. Sci. Total Environ. 757, 12.
- Tang et al., 2023
- Tang, J., Li, W., Chiu, T.Y., Martínez-Peña, F., Luo, Z., Chong, C.T., Wei, Q., Gazaniga, N., West, T.J., See, Y.Y., Lairson, L.L., Parker, C.G., Baran, P.S., 2023. Synthesis of portimines reveals the basis of their anti-cancer activity. Nature 622(7983), 507-513.
- Gorse et al., 2025
- Gorse, L., Plessis, L., Wearne, S., Paradis, M., Pinilla, M., Chua, R., Lim, S.S., Pelluz, E., TOH, G.-A., Mazars, R., Bomfim, C., Hervé, F., Lhaute, K., Réveillon, D., Suire, B., Ravon-Katossky, L., Benoist, T., Fromont, L., Péricat, D., Neil Mertens, K., Derrien, A., Terre-Terrillon, A., Chomérat, N., Bilien, G., Séchet, V., Carpentier, L., Fall, M., Sonko, A., Hakim, H., Sadio, N., Bourdeaux, J., Cougoule, C., Henras, A.K., Perez-Oliva, A.B., Brehmer, P., Roca, F.J., Zhong, F.L., Common, J., Meunier, E., Hess, P., 2025. Portimine A toxin causes skin inflammation through ZAKα-dependent NLRP1 inflammasome activation. EMBO Molecular Medicine 17(3), 535-562.
- Philipp Hess
- Contact