- Recommended name
- Goniodomin A
- Synonyms
- Goniodomin-A
- Recommended acronym
- GDA
- Abbreviation
Progenitors
- Name
- Alexandrium hiranoi
- Name
- Alexandrium taylori
Vector Species
No vector species registered
References
- Structure
-
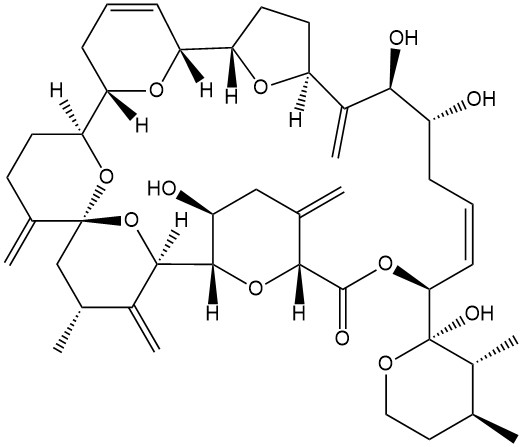
- Formula
- C43H60O12
- Exact mono-isotopic mass
- 768.40848
- Molfile
- see chemfiles
- Alternative molfiles
- n/a
- SMILES
- C=C1CC(O)C2OC1C(=O)OC(C1(O)OCCC(C)C1C)/C=C\CC(O)C(O)C(=C)C1CCC(O1)C1C=CCC(O1)C1CCC(=C)C3(CC(C)C(=C)C2O3)O1
- Alternative SMILES
- n/a
- InChi key
- UBLDAHNUOSMNHW-JYRVWZFOSA-N
- Alternative InChi keys
- n/a
- InChi
- InChI=1S/C43H60O12/c1-22-18-19-49-43(48,28(22)7)36-13-8-10-29(44)37(46)27(6)31-16-17-34(50-31)32-11-9-12-33(51-32)35-15-14-25(4)42(54-35)21-24(3)26(5)39(55-42)40-30(45)20-23(2)38(53-40)41(47)52-36/h8-9,11,13,22,24,28-40,44-46,48H,2,4-6,10,12,14-21H2,1,3,7H3/b13-8-/t22-,24+,28+,29+,30-,31-,32+,33-,34-,35-,36-,37+,38+,39+,40-,42-,43+/m0/s1
- Alternative InChis
- Spectra available
- True
- Chem files
- chemfiles/Goniodomin-A.cdx chemfiles/Goniodomin-A.mol
References
- Murakami et al., 1988
- Murakami, M., K. Makabe, K. Yamaguchi, S. Konosu and M. R. Walchli (1988). "Goniodomin a, a novel polyether macrolide from the dinoflagellate Goniodoma pseudogoniaulax." Tetrahedron Letters 29(10): 1149-1152.
- Harris, 2020
- Harris, C. M., K. S. Reece, D. F. Stec, G. P. Scott, W. M. Jones, P. L. M. Hobbs and T. M. Harris (2020). "The toxin goniodomin, produced by Alexandrium spp., is identical to goniodomin A." Harmful Algae 92: 101707.
- Certified
- False
- Certified links
-
-
n/a
- Non certified reference material
- False
Chemical analysis
- Research
- True
- Standardized
- False
- Validated
- False
- Official
- n/a
Structure recognition assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Functional assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
Animal assays
- Research
- Unknown
- Standardized
- Unknown
- Validated
- Unknown
- Official
- n/a
References
- Krock et al., 2018
- Krock, B., U. Tillmann, Y. Wen, P. J. Hansen, T. O. Larsen and A. J. C. Andersen (2018). "Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of goniodomins A and B and its application to Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax strains and plankton field samples of Danish coastal waters." Toxicon 155: 51-60.
- Regulatory status
- False
- Human toxic syndrome(s)
- n/a
- Organ system toxicity
- n/a
- Risk assessment
- False
- Molecular targets known
- True
- Molecular targets
- F-actin, G-actin
- Toxic to aquatic animals
- Unknown
- TEF available
- False
- Notes
- Several Alexandrium species (A. pseudogonyaulax, A. hiranoi, A.monilatum, A. taylorii, A. ogatae, A. limii) have been proven to produce GDs. Many of these species are linked with fishkills, however GDs have not been conclusively shown to have ichthyotoxicity (Gaillard et al., 2024, Möller et al., 2024). Gaillard, S., Small, H.J., Ayache, N., Tanniou, S., Hess, P., Reveillon, D., Harris, C.M., Harris, T.M., Scott, G.P., MacIntyre, A., Reece, K.S., 2024. Investigating the role of allelochemicals in the interaction between Alexandrium monilatum and other phytoplankton species. Harmful Algae 139, 102706. Möller, K., U. Tillmann, M. Pöchhacker, E. Varga, B. Krock, F. Porreca, F. Koch, T. M. Harris and C. L. Meunier (2024). "Toxic effects of the emerging Alexandrium pseudogonyaulax (Dinophyceae) on multiple trophic levels of the pelagic food web." Harmful Algae 138: 102705. Goniodomin A is quite labile in acidic, alkaline, and even mildly alkaline aqueous solutions, including seawater or culture medium (Harris et al., 2023). GDA is easily transformed into its seco-acid, which is the dominant form in culture supernatant (Harris et al., 2023).
References
- Sharma et al., 1968
- Sharma, G.M., Michaels, L., Burkholder, P.R., 1968. Goniodomin, a new antibiotic from a dinoflagellate. J. Antibiot. 21, 659-664.
- Murakami et al., 1988
- Murakami, M., K. Makabe, K. Yamaguchi, S. Konosu and M. R. Walchli (1988). "Goniodomin a, a novel polyether macrolide from the dinoflagellate Goniodoma pseudogoniaulax." Tetrahedron Letters 29(10): 1149-1152.
- Harris et al., 2020
- Harris, C. M., K. S. Reece, D. F. Stec, G. P. Scott, W. M. Jones, P. L. M. Hobbs and T. M. Harris (2020). "The toxin goniodomin, produced by Alexandrium spp., is identical to goniodomin A." Harmful Algae 92: 101707.
- Harris et al., 2023
- Harris, C.M., Hintze, L., Gaillard, S., Tanniou, S., Small, H., Reece, K.S., Tillmann, U., Krock, B., Harris, T.M., 2023. Mass spectrometric characterization of the seco acid formed by cleavage of the macrolide ring of the algal metabolite goniodomin A. Toxicon 231, 17.